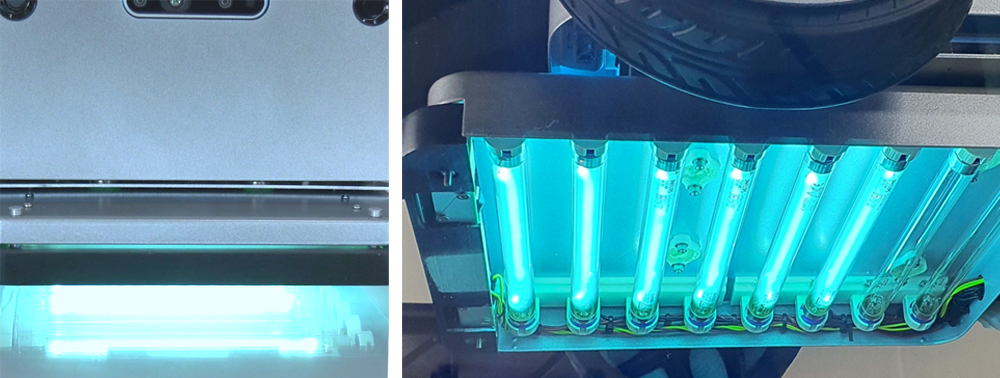
UVC 살균 임무 모듈 설계 제작
- · 살균 대상에 따른 UVC 살균 모듈 설계 기술
- 공간 구조 및 살균 대상 구역
- 살균 가능 시간에 따른 모듈 설계
- UVC 노출 방지를 위한 기술
- · 목적에 맞는 최적 UVC 모듈 설계 기술
- 최적 출력 계산, 요구 램프 및 LED 사양 설계 기술
- 목표 살균력 기준 살균 시간 계산
- UVC 노출 방지를 위한 기술
- · 모바일 로봇을 위한 UVC 램프 구동 회로 제작
UVC
- · 파장 길이가 280 nm 이하로 높은 에너지를 갖는 광선으로 세포내의 DNA와 RNA의 구조를 변화시키는 작용을 합니다.
- · 병원성 바이러스와 세균, 원생생물 모두 DNA와 RNA를 갖고 있으며, UVC는 DNA와 RNA의 구조 변화를 야기하여, 바이러스 등을 비활성화하여 살균작용을 합니다.
UVC 살균 효과
- · UVC 살균 효과는 UVC 빛의 강도가 빛을 조사하는 시간 동안 적산되는 양으로 결정됩니다. 적산광량 = 빛의 강도 x 조사시간
- · 로타바이러스(Rotavirus SA-11)의 경우 90% 살균에 9.1 mJ/cm2, 99.999% 살균에 48 mJ/cm2 가즉, 10 mW 출력의 UVC LED를 사용할 경우 LED와 시료가 이격거리가 거의 없을 경우 1초의 시간이면 1 제곱센티 미터 내의 모든 로타바이러스를 90% 살균할 수 있으며, 99.999%를 살균하기 위해서는 약 5초가 소요됩니다.
그러나 자외선의 광량은 거리의 제곱에 반비례하며, 그늘 지거나 반사되는 광량이 있어, 실제 가해지는 UVC량은 살균 모듈 설계에 따라 크게 차이가 날 수 있습니다.
표그림


출처 : Chevrefils, Gabriel, et al. "UV dose required to achieve incremental log inactivation of bacteria, protozoa and viruses." IUVA News 8.1 (2006): 38-45.
※ UVC 살균 효과 관련 참고문헌
Sommer, R., Pribil, W., Appelt, S., Gehringer, P., Eschweiler, H., Leth, H., Cabaj, A. and Haider, T. 2001. Inactivation of bacteriophages in water by means of non-ionizing (UV-253.7 nm) and ionizing (gamma) radiation: A comparative approach, Wat. Res., 35(13): 3109- 3116.
Lazarova,V. and Savoye, P. 2004. Technical and sanitary aspect of wastewater disinfection by ultraviolet irradiation for landscape irrigation, Wat. Sci. Technol., 50(2): 203-209.
Sommer, R., Weber, G., Cabaj, A., Wekerle, J., Keck, G., and Schauberger, G. 1989. UV inactivation of microorganisms in water. Zbl. Hyg. 189: 214-224.
Husman, A.M.D., Bijkerk, P., Lodder, W., Van den Berg, H., Pribil, W., Cabaj, A., Gehringer, P., Sommer, R. and Duizer, E. 2004. Calicivirus inactivation by nonionizing 253.7-nanometer-wavelength (UV) and ionizing (Gamma) radiation, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 70(9): 5089-5093.
Thurston-Enriquez, J.A. , Haas, C.N. , Jacangelo, J. , Riley, K. and Gerba, C.P. 2003. Inactivation of feline calcivirus and adenovirus type 40 by UV radiation, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 69(1): 577-582.
Gerba, C.P., Gramos, D.M. and Nwachuku, N. 2002. Comparative inactivation of enteroviruses and adenovirus 2 by UV light, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 68(10): 5167-5169.
Thompson, S.S., Jackson, J.L., Suva-Castillo, M., Yanko, W.A., Jack, Z.E., Kuo, J., Chen, C.L., Williams, F.P. and Schnurr, D.P. 2003. Detection of infectious human adenoviruses in tertiary-treated and ultraviolet-disinfected wastewater, Wat. Environ. Res., 75(2): 163-170.
?Meng, Q.S. and Gerba, C.P. 1996. Comparative inactivation of enteric adenoviruses, poliovirus and coliphages by ultraviolet irradiation, Wat. Res., 30(11):2665-2668.
Wilson, B.R., Roessler, P.F., Van Dellen, E., Abbaszadegan, M. and Gerba, C.P. 1992. Coliphage MS-2 as a UV water disinfection efficacy test surrogate for bacterial and viral pathogens, Proceedings, Water Quality Technology Conference, Nov 15-19, 1992, Toronto, Canada, pp. 219-235, Amer. Wat. Works Assoc., Denver, CO.
Liltved, H. and Landfald, B. 1996. Influence of liquid holding recovery and photoreactivation on survival of ultraviolet-irradiated fish pathogenic bacteria, Wat. Res., 30(5): 1109-1114.
Giese, N. and Darby, J. 2000. Sensitivity of microorganisms to different wavelengths of UV light: implications on modeling of medium pressure UV systems, Wat. Res., 34(16): 4007-4013.
Hoyer, O. 1998. Testing performance and monitoring of UV systems for drinking water disinfection, Wat. Supply, 16(1-2): 424-429.
Wu, Y., Clevenger, T. and Deng, B. 2005. Impacts of goethite particles on UV disinfection of drinking water, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 71(7): 4140-4143.
Sommer, R., Haider, T., Cabaj, A., Pribil, W. and Lhotsky, M. 1998. Time dose reciprocity in UV disinfection of water, Water Sci. Technol., 38(12): 145-150.
Otaki, M., Okuda, A., Tajima, K., Iwasaki, T., Kinoshita, S. and Ohgaki, S. 2003. Inactivation differences of microorganisms by low pressure UV and pulsed xenon lamps, Wat. Sci. Technol., 47(3): 185-190.
Tosa, K. and Hirata, T. 1999. Photoreactivation of enterohemorrhagic E. coli following UV disinfection, Wat. Res., 33(2): 361-366.
Oguma, K., Katayama, H. and Ohgaki, S. 2004. Photoreactivation of Legionella pneumophila after inactivation by low- or medium-pressure ultraviolet lamp, Wat. Res., 38(11): 2757-2763.
Yaun, B.R., Sumner, S.S., Eifert, J.D. and Marcy, J.E. 2003. Response of Salmonella and E. coli O157:H7 to UV energy, J. Food Protection, 66(6): 1071-1073.
Chang, J.C.H., Osoff, S.F., Lobe, D.C., Dorfman, M.H., Dumais, C.M., Qualls, R.G. and Johnson, J.D. 1985. UV inactivation of pathogenic and indicator microorganisms, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 49(6): 1361-1365.
Harris, G.D., Adams, V.D., Sorensen, D.L. and Curtis, M.S. 1987. Ultraviolet inactivation of selected bacteria and viruses with photoreactivation of the bacteria, Wat. Res., 21(6): 687-692.